What is WebSailor?
On the 11th of July, Alibaba’s Tongyi Lab has launched WebSailor, an open-source platform that’s pushing the boundaries of what AI agents can do online. In a space long dominated by closed systems like DeepResearch and Doubao, WebSailor is showing that open-source can compete (and even lead) when it comes to advanced web reasoning.
At its core, WebSailor helps AI agents do something really hard: make sense of messy, ambiguous, and uncertain information from across the internet. To train agents for this challenge, the team created tasks that simulate real-world complexity, blending structured sampling, clever information obfuscation, and a custom reinforcement learning method called DUPO (Duplicating Sampling Policy Optimization). The result is agents that think more strategically, search more efficiently, and solve problems that would stump even experienced humans.
How does WebSailor compare?
WebSailor’s models, ranging from 3B to 72B parameters, have performed exceptionally well on difficult benchmarks like BrowseComp-en/zh. In fact, the largest WebSailor models now rival or beat top proprietary systems. That’s a big deal for anyone building AI tools that need to go beyond basic question answering, into the territory of deep research, synthesis, and real-world decision-making.
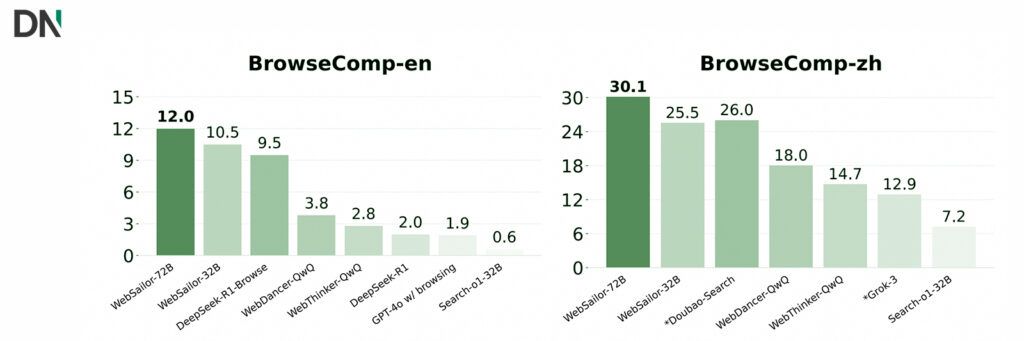
Even more impressively, WebSailor isn’t just good at hard tasks. It also holds up on easier benchmarks, proving that its training approach builds general skills, not just tricks for specific tests.
For researchers, developers, and companies interested in building capable and transparent AI systems, WebSailor offers a powerful, and freely available, foundation. You can dive into the details in their recent paper on arXiv, or explore the project on GitHub: Alibaba-NLP/WebAgent.






