The journey of Artificial Intelligence has been marked by significant milestones, from rule-based systems to machine learning algorithms, neural networks, and advanced language models – like ChatGPT, for example. Each advancement has brought us closer to creating machines that can think and act like humans. However, agentic AI (also known as agentic systems) represents a remarkable step in this evolution, moving beyond pre-programmed responses to exhibit truly autonomous behavior in real-world environments.
Agentic AI is not just another incremental improvement in AI technology; it represents a fundamental shift in how we conceptualize and implement complex systems. These autonomous systems are designed to operate with a level of independence and decision-making capability that closely mimics human cognitive processes. These capabilities open up new possibilities for automation, innovation, and strategic decision-making across a wide range of industries.
What Is Agentic AI?
At its core, Agentic AI refers to advanced Artificial Intelligence entities capable of independent decision-making, planning, and adaptive execution to complete complex processes and achieve specific objectives. Unlike traditional AI systems that operate within rigid, predefined parameters, agentic AI demonstrates a remarkable ability to understand context, set goals, and adjust its actions based on environmental feedback.
Key characteristics that define agentic AI include:
- Autonomy: The ability to operate independently with minimal human supervision.
- Reasoning and Decision-Making: Advanced capabilities to analyze situations, weigh options, and determine appropriate actions.
- Goal-Oriented Behavior: The capacity to set and pursue objectives, breaking down complex tasks into manageable steps.
- Adaptability: Flexibility to adjust strategies and behaviors based on new information or changing circumstances.
- Natural Language Processing: Comprehension and generation of complex instructions in human language.
- Workflow Optimization: Efficient execution and management of multi-step processes.
To illustrate the difference between agentic AI and conventional AI, consider a traditional chatbot versus an agentic customer service AI. While a chatbot can provide pre-programmed responses to specific queries, an agentic system can understand the context of a customer’s problem and devise a multi-step solution. It interacts with various company systems to implement that solution, and learns from the experience to improve future interactions. For a more clear understanding of what agentic systems are, let’s examine them in comparison to generative AI.
Agentic AI vs. Generative AI: Understanding the Distinction
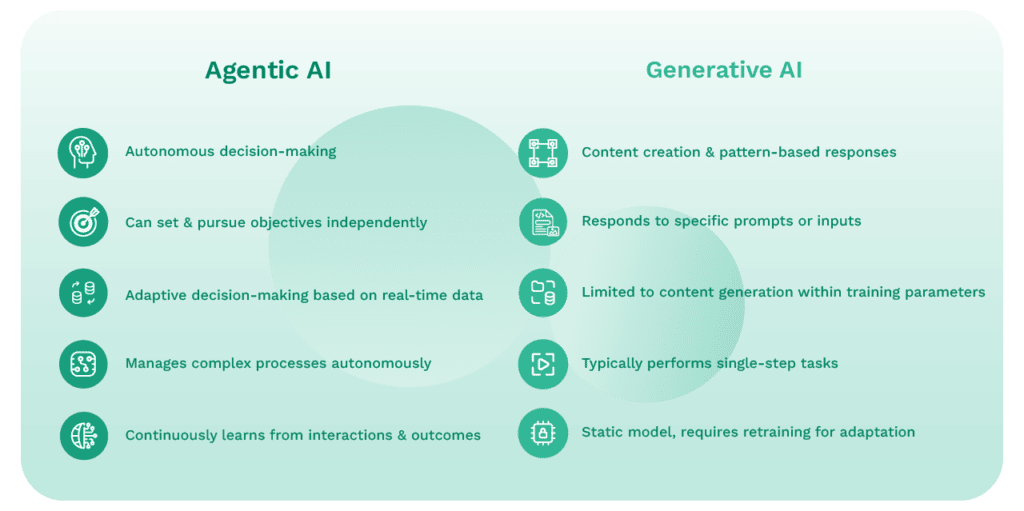
While both agentic AI and generative AI represent significant advancements in Artificial Intelligence, they serve different purposes and have distinct capabilities. Understanding these differences can help distinguish in which cases Agentic AI systems positively improve your automation.
Generative AI: Creating Content
Generative AI, commonly being used by large language models like GPT-4o and DALL-E 3, focuses on creating new content based on patterns learned from vast datasets. These systems can:
- Generate human-like text, images, or other media
- Complete prompts or answer questions based on learned information
- Assist in creative tasks like writing, design, or coding
However, Generative AI typically operates within the boundaries of its training data and doesn’t possess true decision-making capabilities or goal-oriented behavior.
Agentic AI: Autonomous Decision-Making and Action
In contrast, agentic AI is designed for autonomous decision-making and action in complex, real-world environments. Key differences include:
- Goal-Oriented Behavior: Agentic AI can set and pursue objectives independently, breaking them down into actionable steps.
- Contextual Decision-Making: These systems can analyze situations, weigh options, and make decisions based on real-time data and changing circumstances.
- Adaptive Learning: Agentic AI continuously learns from its interactions and outcomes, improving its performance over time.
- Multi-Step Task Execution: Unlike generative AI, which typically performs single-step tasks, agentic AI can manage complex, multi-stage processes autonomously.
- Integration with External Systems: Agentic AI can interact with various business systems and data sources to execute tasks and make informed decisions.
Complementary Technologies
While distinct, Agentic AI and Generative AI can be complementary to each other. For instance, an agentic system might leverage Generative AI capabilities to produce human-like responses or creative solutions as part of its decision-making process. This combination can lead to more sophisticated and versatile AI applications in business contexts.
Why Is Agentic AI Important for Organizations?
Agentic AI is becoming increasingly important for organizations due to its ability to autonomously manage tasks, make decisions, and adapt to changing environments, which can significantly enhance operational efficiency and innovation. Here are some key reasons why agentic AI is crucial for modern enterprises:
- Increased Efficiency: Automates complex workflows, reducing costs and boosting productivity.
- Better Decision-Making: Analyzes data to provide insights for informed strategic choices.
- Adaptability: Quickly adjusts strategies in response to market changes.
- Scalable Personalization: Delivers tailored experiences to customers and employees.
- Innovation Driver: Frees up time for creative and strategic work, fostering innovation.
- Competitive Edge: Early AI adoption enhances efficiency and market responsiveness.
Real-Life Applications and Examples
The potential applications of agentic AI span across various industries and business functions. Here are some real-life examples that demonstrate its versatility and impact:
Healthcare and Personalized Medicine
In healthcare, an agentic AI could act as a personal health assistant, continuously monitoring patient data from wearable devices, adjusting treatment plans based on real-time health indicators, scheduling appointments when necessary, and even predicting potential health issues before they become serious. For instance, IBM Watson Health uses AI to analyze patient data for cancer treatment. The platform provides personalized treatment recommendations based on medical histories and diagnostic tests, enhancing the accuracy and speed of diagnoses.
Retail
There are numerous companies implementing agentic AI into their operations in the retail sector. Indicatively, Amazon employs Kiva robots, now known as Amazon Robotics in its warehouses to autonomously manage inventory placement and order fulfillment. These robots optimize warehouse operations by making decisions about resource allocation, thereby increasing efficiency.
Another fast-fashion retailer, Zara, uses agentic AI for supply chain management. Specifically, agentic AI is being used to predict demand fluctuations and streamline inventory management. This allows for rapid response to market changes and efficient handling of seasonal product launches.
Energy Management
Google Deepmind utilized agentic AI for Smart Grid Management. Google DeepMind’s AI system optimizes energy usage in data centers by making autonomous decisions that balance objectives such as energy efficiency and equipment lifespan.
Autonomous Vehicles and Robotics
Agentic AI is at the heart of autonomous vehicle technology. These AI agents must make split-second decisions based on complex environmental data, predict the behavior of other road users, and adapt to unexpected situations in real-world environments. Similar principles apply to advanced robotics in manufacturing and warehouse automation. The example mentioned above about Amazon’s Robotics attests to such uses of agentic systems.
Financial Services and Trading
In the financial sector, agentic AI can manage investment portfolios autonomously, making real-time trading decisions based on market analysis, economic indicators, and risk assessments. These systems can process vast amounts of data much faster than human traders, potentially identifying opportunities and mitigating risks more effectively. For example, Two Sigma uses AI-driven trading algorithms that analyze market data, make trading decisions, and adjust strategies in real-time. This demonstrates goal-oriented behavior in a complex financial environment.
Another example is JPMorgan Chase’s COiN Platform. JPMorgan Chase has implemented the COiN platform to automate back-office operations such as data entry and compliance checks, improving efficiency and accuracy in processing financial documents.
Transportation and Logistics
In the transportation sector, Waymo employs agentic AI in its self-driving cars, which make real-time decisions based on complex environmental data. These vehicles demonstrate goal-directed behavior and adaptability to unpredictable situations, enhancing transportation safety and efficiency.
UPS uses the ORION platform to optimize delivery routes. This AI-powered system analyzes data from multiple sources, including traffic patterns and weather conditions, to generate efficient delivery routes, improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Cybersecurity
Darktrace, a British cybersecurity company, employs agentic AI to continuously monitor network traffic and identify cybersecurity threats. The AI agents autonomously initiate responses to detected threats, providing real-time defense without human intervention.
Challenges and Considerations of Agentic AI
Agentic AI presents a range of challenges that organizations must navigate to successfully implement and manage these systems. These challenges share some similarities with those faced by generative AI, but there are also distinct differences due to the nature and applications of each technology. In detail:
- Complexity and Unpredictability: Agentic AI systems can become extremely complex, making their behavior difficult to predict or control, especially in new situations. This unpredictability can lead to unforeseen consequences, which is a critical issue in ensuring safety and reliability.
- Integration Complexity: While generative AI often focuses on content creation (e.g., text, images), agentic AI involves integrating autonomous decision-making into business processes, which can be more complex due to the need for seamless interaction with existing systems. Also, incorporating agentic AI into established business processes and legacy systems can be technically challenging and disruptive.
- Data Requirements & Computational Resources: Similarly to Gen AI, agentic systems often require vast amounts of diverse, high-quality data for training, which can be challenging and costly to obtain. Additionally, training and running agentic AI models typically demand significant computational power, potentially requiring substantial infrastructure investments.
- Explainability and Transparency: As these systems become more complex, understanding and explaining their decision-making processes becomes increasingly difficult, which can be problematic in regulated industries or when transparency is required.
- Ethical & Regulatory Concerns: Agentic AI’s ability to make autonomous decisions in critical applications (e.g., healthcare, finance) may face stricter regulatory scrutiny compared to generative AI used primarily for creative tasks. It also raises ethical concerns due to its potential for unintended consequences of autonomous decision-making.
- Autonomy and Control: Agentic AI systems are designed to operate autonomously with minimal human intervention, which introduces unique challenges related to control and oversight that are less pronounced in generative AI applications.
The Future of Agentic AI
What does the future of Agentic AI look like? As AI is constantly evolving, we cannot help but think what its impact will be. Let’s take a look:
- Increased Autonomy and Efficiency: Agentic AI systems will continue to evolve, becoming more autonomous and capable of handling complex, decision-intensive tasks without human intervention. This will enhance efficiency across industries, allowing businesses to focus on strategic initiatives and creative problem-solving.
- Integration with IoT: The integration of agentic AI with the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization of operations across sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation. This could lead to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved safety.
- Multi-Agent Systems: The rise of multi-agent systems will enable AI agents to collaborate on complex tasks by dividing responsibilities among different agents. This collaboration will require robust mechanisms for verification, validation, and feedback to ensure reliable outcomes.
- Continuous Improvement and Adaptability: Agentic AI systems will become more adaptable, continuously learning from new data and experiences to improve their performance over time.
- Regulatory Frameworks: As agentic AI becomes more integrated into daily life, regulatory frameworks will need to evolve to ensure the safe and ethical use of these systems. Stricter regulations are expected to govern AI’s deployment in critical areas like healthcare and finance.
In summary, the future of agentic AI holds immense potential for transforming industries through enhanced autonomy, efficiency, and adaptability.
How Can You Benefit from Agentic AI Systems?
Agentic AI represents a significant step in artificial intelligence, offering remarkable levels of autonomy and problem-solving capabilities. For organizations, understanding and leveraging this technology is necessary as it enables more efficient operations, better decision-making, and new avenues for innovation.
Are you interested in exploring how agentic AI can be useful for your organization? Contact DataNorth and one of our AI Experts can guide you through! We offer AI Assessments in order to determine how and what AI technologies can be beneficial to your organization. If you are interested in enhancing your employees’ skills in AI, you can choose from our AI training and workshops.