Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the way we live and work, making it a crucial skill to understand in 2025. From automating mundane tasks to enhancing decision-making, AI’s capabilities are vast and growing.
In this guide, we’ll explore what AI is, what it isn’t, its types, and its advantages and disadvantages. Whether you’re new to AI or looking to deepen your knowledge, this is your starting point.
If you are already familiar with the basics of AI, you can skip the first part of the blog and go directly to the first steps in AI. Let’s get started on learning AI!
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
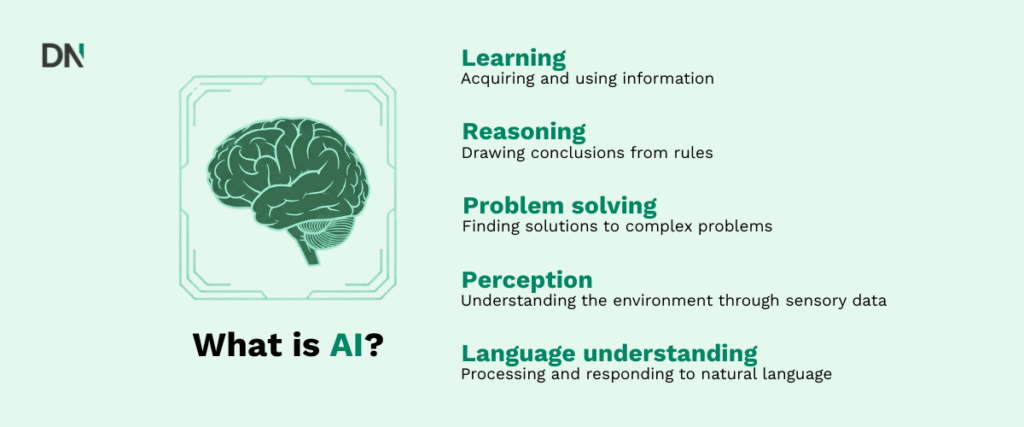
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a field in computer science focused on creating machines that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence. These tasks include:
- Learning: Acquiring and using information.
- Reasoning: Drawing conclusions from rules.
- Problem solving: Finding solutions to complex problems.
- Perception: Understanding the environment through sensory data.
- Language understanding: Processing and responding to natural language.
AI systems use techniques like machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks to achieve these abilities. This allows them to learn from experience, adapt to new inputs, and perform tasks similar to humans.
However, the definition of AI can be complex and sometimes controversial. Let’s look at what is generally considered AI and what is not, along with some examples.
What is considered AI
Artificial intelligence is an ever-evolving field that defines a wide array of technologies capable of performing tasks that typically require human-like intelligence.
Here are some prominent examples of AI:
- Machine learning: Systems that learn and improve from experience without explicit programming. For example, Netflix’s recommendation system suggests movies and TV shows based on user behavior.
- Computer vision: Systems that interpret visual information. Facial recognition systems in security and smartphone unlocking are some examples where computer vision is implemented.
- Expert systems: AI that mimics human decision-making. Such systems are medical diagnosis systems that analyze symptoms and suggest conditions.
- Robotics: AI-powered robots that perform complex tasks and interact with their environment. Think of autonomous vehicles and industrial robots in manufacturing.
What isn’t considered AI?
It is easy to misinterpret which systems are actually powered by AI technology. Here are some examples of what isn’t considered AI:
- Simple automation: Programs that follow pre-defined rules without learning or adapting. For example, a basic calculator or a thermostat with set temperatures is not considered AI.
- Data analysis tools: Software that processes data but doesn’t learn or make decisions. Think of basic spreadsheet applications or simple data visualization tools.
- Basic search engines: Systems that only match keywords without AI. For instance, a simple database query returning exact matches.
- Hard-coded decision trees: Fixed if-then rule systems that can’t learn. Such an example would be a basic chatbot with pre-written responses.
- Traditional computer programs: Software that performs specific tasks based on explicit instructions without improving. A word processor or a video game with predetermined responses is such a program that does not encompass AI technology.
It is evident that the lines between AI and non-AI systems can be blurry, especially as technology advances. Many modern systems combine AI with traditional programming, creating hybrid approaches. As AI evolves, our understanding of what is being considered AI may change, with new techniques and applications emerging regularly.
After clearing up the setting between what and what is not considered AI, let’s delve into the advantages and disadvantages when it comes to AI.
The advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers numerous benefits that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and capabilities across various fields. Here’s a list of some of the most important advantages AI offers:
- Increased efficiency and productivity: AI can automate repetitive tasks and do them faster than humans, allowing people to focus on more complex work.
- Reduction in human error: AI performs tasks with high precision and accuracy, reducing mistakes caused by human fatigue or other factors.
- Available 24/7: AI systems can work continuously without needing breaks or sleep.
- Enhanced decision-making: AI quickly analyzes large amounts of data to identify patterns and trends, helping businesses make better decisions.
- Improved customer experiences: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide personalized, round-the-clock customer support. With DataNorth’s AI Chatbot for customer service, you can achieve this effortlessly.
- Advanced data analysis: AI processes and analyzes massive amounts of data to uncover insights that humans might miss.
It’s important to note that while AI offers many advantages, it also presents potential drawbacks and ethical considerations that need careful attention as the technology evolves and spreads across various industries.
The disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Despite its advantages, AI also presents several challenges and drawbacks:
- High implementation costs: Setting up AI systems requires significant financial investment due to the complex engineering involved and expensive hardware/software requirements.
- Lack of creativity, emotional intelligence and human judgement: AI lacks the ability to think creatively or understand emotions in the way humans do. It cannot truly replicate human creativity, empathy, or out-of-the-box thinking. It is also unable to make ethical decisions or understand context in the same way humans can, which can be problematic in complex or nuanced situations.
- Potential job displacement: As AI automates more tasks, there are concerns about job losses in certain sectors, particularly for repetitive or routine jobs.
- Lack of transparency: Many AI systems, especially complex machine learning models, operate as “black boxes” where it’s difficult to understand how they arrive at decisions. This lack of explainability can be problematic, especially in sensitive applications like criminal justice.
- Bias and discrimination: AI systems can perpetuate or amplify existing biases if trained on biased data or designed with inherent biases.
- Privacy and security concerns: The use of AI often involves collecting and analyzing large amounts of personal data, raising privacy issues. Additionally, AI systems can be vulnerable to hacking or malicious use.
It’s important to note that while these disadvantages exist, many researchers and companies are actively working to address these challenges as AI technology continues to evolve.
The different types of Artificial intelligence
To begin with, AI can be classified in several ways, such as by capabilities, functionality, or underlying technology.
Here are of the common categorizations and their differences:
Based on capabilities
We have three categories when classifying AI based on their capabilities, these are:
- Narrow AI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence, ANI): This type of AI is designed to perform a single task or a set of closely related tasks. It operates under a limited pre-defined range or context and cannot go beyond its programmed area. Examples include chatbots and recommendation systems. Most AI in use today is Narrow AI.
- General AI (Artificial General Intelligence, AGI): AGI refers to a level of AI that can understand, learn, and apply knowledge in a way that is indistinguishable from human intelligence. It can perform any intellectual task that a human being can. AGI can transfer knowledge between domains and adapt its learning to new problems. This type of AI is still theoretical and does not yet exist in practice.
- Super AI (Artificial Superintelligence, ASI): Beyond AGI lies ASI—a stage of AI where machines surpass human intellect in every aspect: creativity, general wisdom, and problem-solving. Super AI remains a concept from science fiction and philosophical discourse, with no practical examples as of my knowledge cutoff in 2023.
Based on functionality
There are four types of AI on the basis of functionality. Let’s get into more detail:
- Reactive machines: These AI systems have no memory and are designed to respond to specific stimuli or inputs. They react to situations using predefined algorithms. IBM’s Deep Blue chess computer is an example.
- Limited memory: This AI classification includes machines that can learn from historical data to make decisions. Most present-day AI applications, like self-driving cars or chatbots, fall into this category as they utilize large amounts of data to learn and improve over time.
- Theory of mind: This is a future class of AI that not only understands and remembers information but also has the ability to recognize and process emotions, beliefs, and thoughts (i.e., it attributes mental states to others). It’s considered a crucial step towards AGI.
- Self-aware AI: This is the highest level of AI, where machines have their own consciousness and self-awareness. This type of AI is still theoretical and lies in the realm of futurology and speculative fiction.
Based on technology
Lastly, AI can be classified depending on the technology implemented, hence, we have the following categories:
- Machine learning (ML): AI systems capable of learning from data, identifying patterns, and making decisions with minimal human intervention fall into this category. ML includes subfields like supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- Deep learning: a machine learning technique that uses artificial neural networks to analyze large datasets. It helps solve complex problems, such as natural language processing and image recognition (e.g., self-driving cars).
- Neural networks: A subset of ML, these are AI systems designed to simulate the human brain’s interconnected neuron structure. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are examples of this.
- Natural language processing (NLP): AI systems that understand, interpret, and generate human language fall into this category. This can range from basic chatbot interactions to sophisticated systems that can interpret context, humor, and emotion.
- Robotics: This field combines AI with mechanical engineering, electronics, and computer science to create machines capable of performing various tasks. Robotics can include AI systems with very narrow tasks to more complex ones that interact with the physical world adaptively.
Why is Artificial Intelligence so popular in 2025?
AI has become incredibly popular in 2025 due to several key factors and innovations:
- Advancements in generative AI: Generative AI models like GPT-4o have become more powerful and versatile, expanding beyond text to include multimodal capabilities with images, audio, and video. Tools like Suno for AI-generated music, Runway Gen-3 for high-quality video synthesis, and Midjourney v6 for hyper-realistic image generation have expanded the boundaries of what’s possible. This has opened up new creative and practical applications across industries.
- Increased accessibility and customization: AI tools are becoming more user-friendly and customizable, allowing non-technical users to create their own AI applications. Companies like Google and OpenAI are developing platforms that enable people to build custom chatbots and AI models without coding skills.
- Integration into everyday technologies: AI is being seamlessly incorporated into common devices and software, from smartphones to productivity tools, making it a ubiquitous part of daily life.
- Business adoption: More companies are integrating AI into their operations, with 83% of businesses claiming AI is a top priority in their plans. This widespread adoption is driving innovation and creating new use cases.
- AI for personalization and customer experience: Businesses are leveraging AI to provide highly personalized products, services, and marketing campaigns to improve customer experiences. For example, Lily AI uses image recognition to assign descriptors to products in fashion, home, and beauty spaces, improving product discovery and recommendations.
- Advancements in specialized fields: AI is making significant strides in areas like healthcare (disease detection, drug discovery), scientific research (climate modeling, material science), and autonomous systems (self-driving cars).
- Small language models (SLMs): These more compact AI models are gaining traction as they offer improved efficiency and can run on devices with limited resources.
- Ethical AI and regulation: There’s an increased focus on developing responsible AI systems and implementing regulations to address concerns about bias, privacy, and societal impact
Why is it important to start learning about and using AI in 2025?
There are lots of reasons why it’s crucial to start learning about and using AI in 2025. Here are some reasons of why it’s important to start learning about and using AI in 2025:
- Competitive advantage: AI adoption is rapidly increasing, with 73% of US companies already using AI in some areas of their business. Those who don’t embrace AI risk falling behind competitors who are leveraging it to improve efficiency, decision-making, and customer experiences.
- Improved operational efficiency: AI can automate repetitive tasks, optimize processes, and streamline operations. For example, AI-powered supply chain optimization can reduce costs and improve delivery times. This allows businesses to allocate resources more effectively and focus on strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced decision-making: AI analyzes vast amounts of data to provide actionable insights and predictions. This enables more informed, data-driven decision-making across various business functions, from financial planning to marketing strategies.
- Personalized customer experiences: AI enables businesses to offer highly personalized products, services, and marketing campaigns. This improves customer satisfaction and loyalty, with 80% of consumers preferring brands that provide personalized experiences.
- Cost savings: Implementing AI can lead to significant cost reductions. For instance, chatbots and virtual assistants can handle routine customer inquiries, reducing the need for human customer service representatives.
- Revenue growth: AI has the potential to substantially increase profitability. By 2035, AI is projected to increase corporate profitability in 16 industries by an average of 38%.
- Innovation and new business models: AI opens up opportunities for creating innovative products, services, and business models that weren’t previously possible.
- Talent attraction and retention: As AI becomes more prevalent, employees with AI skills will be in high demand. Learning about AI can make you more valuable to your organization and open up new career opportunities.
- Improved risk management: AI can help detect fraud, identify potential cybersecurity threats, and improve overall risk assessment and management.
By starting to learn about and implement AI now, you can position yourself and your organization to take full advantage of this transformative technology, driving growth, efficiency, and innovation in the years to come.
How to start learning about and using AI step-by-step?
As a professional in business, you can start learning about and using AI step-by-step with this approach:
- Familiarize yourself (and your team) with AI concepts: Begin by understanding basic AI terminology and concepts. This will help you grasp the potential applications in your field. You could start by reading AI guides (as the one you are reading now!) or follow online courses and AI training courses, introducing you to AI.
For a deep understanding of AI technology and how to effectively implement it in your organization, opt for participating in AI workshops. DataNorth offers AI workshops that can help your organization get started with AI. - Identify potential use cases: Look for areas in your work where AI could improve efficiency or provide insights. For example, in email automation or in the optimization of HR processes.
- Start with user-friendly AI tools: There is a wide variety of tools available online; begin with accessible tools like ChatGPT to get hands-on experience. Also, DataNorth has created an AI Tools Cheat Sheet to help you familiarize and explore some of the latest and most trending AI Tools that have been developed.
- Experiment and learn: Try out AI tools in low-stakes situations to understand their capabilities and limitations.
- Stay informed: Follow AI news and developments in your industry to keep up with the latest trends. Do this by following relevant people on LinkedIn or sign up for a newsletter about AI.
- Consult with AI-experts: Talk with AI experts to see how you have AI make an impact in your organization. DataNorth offers, among other AI services, AI Consultancy to help you identify and implement AI solutions, improving your organization’s efficiency.
Looking for inspiration for your first AI project? Here is a simple use case to get you started.
Use-case: ChatGPT for crafting marketing emails
- Start by opening ChatGPT (either at chat.openai.com or through a business account); it will be used as your writing tool.
- Provide a prompt like: “Draft a marketing email for our new product launch. The product is a smart water bottle that tracks hydration levels. Target audience is health-conscious professionals aged 25-45.”
- Review the generated content and refine it as needed.
- Use follow-up prompts to improve specific aspects, such as “Make the tone more casual” or “Add a call-to-action at the end.”
This exercise will give you a practical understanding of how AI can assist with content creation and how to interact with AI tools effectively.
However, it is important to note that you need to be precise and concrete when engineering your prompt, in order to get the expected outcomes. Download DataNorth’s Prompt Engineering Cheat Sheet to improve your ability in crafting effective prompts.
AI is no longer just a concept of the future; it’s a vital tool driving innovation and efficiency across various industries. By understanding and leveraging AI, you can stay ahead of the curve, enhance your professional skills, and unlock new opportunities. Dive into AI today and start transforming your approach to business and technology, contact DataNorth for an AI Consultancy and step into the transformative world of AI.