Nowadays, businesses generate more data than ever before, yet transforming that data into meaningful insights remains challenging. For many companies, the overwhelming volume and complexity of data make it essential to find solutions that simplify and deepen analysis.
To meet this need, data analytics keeps evolving. Simple Data Analytics (SDA) continues to serve essential needs, while now, with the introduction of AI in recent years, Intelligent Data analytics (IDA) has been introduced as a powerful tool for uncovering deeper insights and addressing more complex challenges.
What are their key features? What are their use cases?
In this blog, we will explore the difference between simple data analytics and intelligent data analytics.
What is Simple Data Analytics?
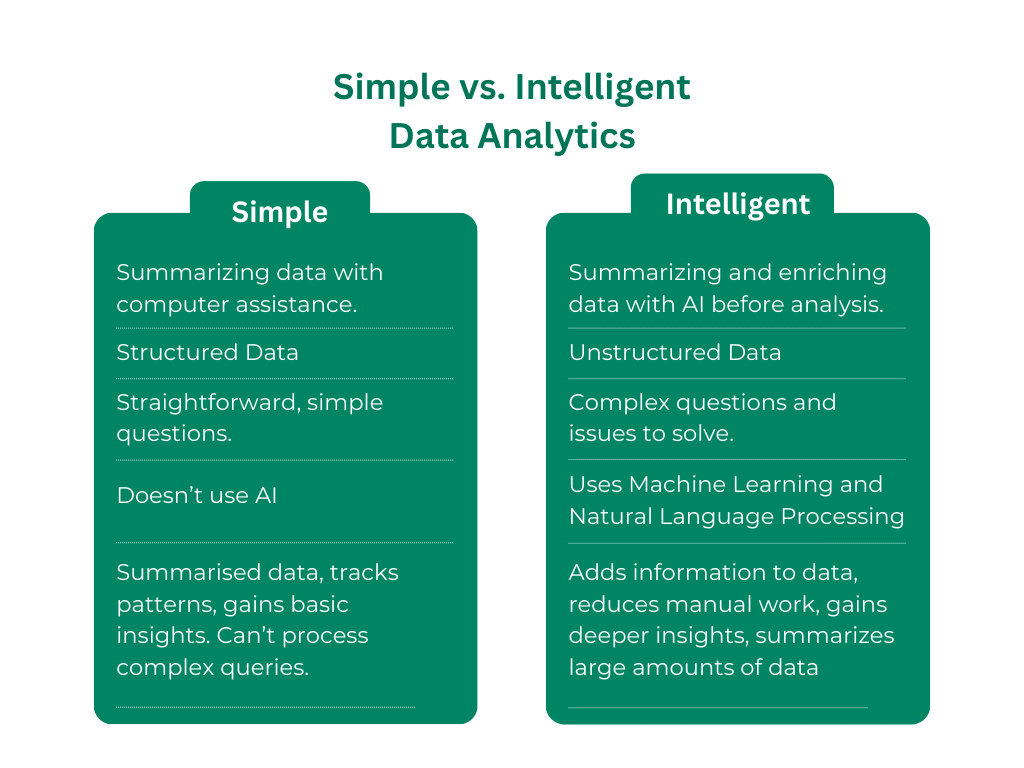
Simple Data Analytics is a method of data analysis provides a high-level overview that might help organizations understand general insights without involving complex algorithms and tools.
Techniques Used in SDA:
- Basic Statistics: Calculations like averages, percentages, and totals give a snapshot of trends or performance.
- Charts and Graphs: Visual representations—like bar charts, line graphs, or pie charts—make patterns in the data easy to see at once.
- Trend Analysis: Observing changes over time helps teams quickly spot trends, such as monthly sales increases or seasonal shifts in customer behavior.
Strengths and Benefits of Simple Data Analytics
Simple Data Analytics offers several strengths that make it an attractive choice for many organizations. From providing quick insights to being highly cost-effective, SDA helps teams extract value from their data without requiring advanced expertise. Here’s a look at its key benefits.
1. Accessible and Clear
By focusing on foundational techniques, SDA provides clarity, which makes it ideal for teams without extensive data expertise.
2. Quick Insights
Simple analytics allows teams to identify important patterns and spot any unusual data without delay. For example, it can quickly show if a specific product is selling faster than others.
It provides a high-level overview of operations, like total sales, customer counts, or production volumes, making it a valuable tool for initial data exploration
3. Ease of Interpretation
The results are easy for anyone to interpret, regardless of their experience with data. This simplicity ensures that team members from different backgrounds can contribute to data discussions.
4. Cost-Effective
Simple analytics doesn’t require advanced software or technical domain knowledge, so it’s budget-friendly. Many basic analytics tools are inexpensive or even free, which is ideal for businesses with limited resources or teams new to data analytics.
5. Ideal for Initial Insights
Simple analytics is perfect for gaining an initial understanding of current performance, like tracking monthly sales or customer feedback. It’s also useful for quick decisions, such as deciding whether to stock more of a popular product.
Limitations of Simple Data Analytics
While Simple Data Analytics can be effective for basic insights, it comes with several limitations. From missing deeper patterns to lacking predictive power, these drawbacks can hinder businesses from unlocking their full analytical potential. Here’s an overview of the key limitations of SDA.
1. Limited Depth
Simple analytics offers a surface-level view, which can be great for overviews but often falls short when businesses need detailed insights. For example, simple analytics might show a sales decline, but it won’t explain why it’s happening or which factors are driving it.
2. Possible Missed Insights
Because it uses basic methods, simple analytics may miss complex patterns, like subtle customer buying behaviors or relationships between different data points. In large or detailed datasets, these deeper patterns are easily overlooked, which can limit understanding.
3. Predictive Limitations
Simple data analytics doesn’t use advanced algorithms, which are key to predicting future trends. For instance, while it might show past sales data, it can’t accurately forecast future sales or suggest strategies based on predictive patterns.
4. Competitive Drawbacks
In the competitive environment, relying only on simple analytics can mean missing out on deeper opportunities hidden within the data. Without deeper insights, businesses risk falling behind competitors who are using advanced tools to make more strategic, informed decisions.
What is Intelligent Data Analytics?
Intelligent Data Analytics surpasses the traditional method by using AI technologies such as machine learning. This method of data analysis enables businesses to analyze complex datasets in real time, providing deeper data-driven insights.
IDA can identify correlations, make predictions and even automate decision making processes.
Strengths and Benefits of Intelligent Data Analytics
Here are the key advantages of leveraging Intelligent Data Analytics. From uncovering hidden patterns to automating complex processes, IDA empowers organizations to make smarter, faster decisions and stay ahead in a competitive market.
1. Data Enrichment
Intelligent data analytics enhances existing datasets by integrating additional relevant information from various sources. This leads to a more comprehensive understanding of trends and patterns, enabling better decision-making.
2. Unstructured Data Analysis
It excels in processing unstructured data, such as text, images, and social media content, uncovering valuable insights that traditional methods might overlook. This capability allows businesses to enter the wealth of information beyond structured databases.
3. Automated Summarization
Intelligent analytics can automatically summarize large datasets, providing concise and relevant insights at a glance. This saves time and enables teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than sifting through mountains of data.
4. Predictive Analytics
By utilizing advanced algorithms, intelligent data analytics can forecast future trends and outcomes, allowing businesses to stay ahead and make proactive decisions.
5. Reducing Manual Workload
By automating data analysis processes, intelligent analytics significantly reduces manual workload, freeing up employees’ time resources for more strategic tasks.
6. Providing Deeper Insights
The depth of analysis offered by intelligent data analytics enables organizations to answer complex business questions and make informed decisions based on comprehensive data interpretation.
Challenges of Intelligent Data Analytics
As businesses increasingly turn to Intelligent Data Analytics (IDA) for deeper insights, they must also navigate a range of challenges. From the need for specialized expertise to managing complex algorithms, organizations must carefully balance the benefits of IDA with its demands.
1. Need for Specialists
To maximize the benefits of intelligent analytics, businesses often need data scientists and artificial intelligence specialists who can design, implement, and interpret complex models. Hiring in-house talent can lead to increased costs. An alternative is to partner with external experts, like DataNorth, who can provide the necessary skills and insights to maximize your analytics capabilities without the overhead of expanding your team.
2. Complexity of Models
The advanced algorithms used in intelligent data analytics can be complex and difficult to interpret. This may pose challenges for non-technical team members in understanding the insights generated. Engaging external experts to translate complex findings into clear, actionable insights can help ensure that everyone on the team benefits from the data.”
3. Data Quality and Bias
The effectiveness of intelligent analytics relies heavily on the quality of the data being analyzed. If data is biased or inaccurate, the insights produced can lead to flawed conclusions. Not sure about the quality of your data? Consider having it reviewed by external experts for a fresh perspective.
4. Implementation Costs
Implementing intelligent data analytics can require a significant investment in technology and infrastructure, which may be a barrier for smaller organizations. However, this investment provides far deeper insights than SDA, empowering businesses to make smarter, cost-saving decisions in the long run.
Business Examples of Simple and Intelligent Data Analytics
Simple Data Analysis and Intelligent Data Analysis each serve unique roles depending on the complexity and demands of the task. The table below illustrates how these approaches are applied in different industries, highlighting the strengths and limitations of each in specific business scenarios.
| Industry | SDA Application | Explanation | IDA Application | Explanation |
| Retail | Sales Reporting | Basic tracking of incoming stock, total sales, and returns. | Customer Behavior Prediction | Uses AI to predict customer buying patterns |
| Finance | Monthly Statements | Monthly account summaries for clients, showing income and expenses. | Fraud Detection | Detects unusual transaction patterns that may indicate fraud |
| Medicine | Patient Records | Patient information including history, treatments, and test results. | Treatment Optimization | Analyzes large patient datasets to find the most effective treatment plans |
| Manufacturing | Inventory Tracking | Inventory levels tracking and stock movements. | Predictive Maintenance | Uses data from equipment to predict maintenance needs, preventing breakdowns and reducing downtime. |
This comparison demonstrates that while SDA provides essential baseline analytics, IDA offers more advanced, predictive capabilities that can drive proactive and optimized decision-making. Choosing the right approach depends on the specific needs and resources of each business, and understanding these applications can help organizations make the best use of their data.
Simple or Intelligent: Which Data Analysis Method To Use in Your Organization
This framework explores common scenarios involving complexity of data and varying skill levels, providing tailored recommendations to help you make the most of your data. Whether you’re just starting your analytics journey or looking to maximize the impact of an expert team, this section will help you choose the most suitable approach.
1. Moderate Complexity of Data + No In-House Skills
When an organization faces moderate complexity in data analysis (datasets that are manageable in size and scope but still require some structured analysis to reveal patterns or trends) and lacks internal expertise, the recommended approach is Simple Data Analysis. SDA is suited for general questions and basic insights.
- Challenges: Lack of internal expertise may limit data interpretation.
- Goals: Build foundational capabilities for future analysis.
- Recommendation: Use SDA to gain quick insights and progressively train the team
2. Moderate Complexity of Data + Basic Skills
When an organization faces moderate complexity in data analysis and has basic skills in artificial intelligence and data science, the recommended approach is Simple Data Analysis. SDA is suitable for general questions and basic insights.
- Challenges: Limited analytical depth due to basic skills.
- Goals: Enhance analytical capabilities for better insights.
- Recommendation: Use SDA to gain quick insights and progressively train the team through AI consultancy services offered by DataNorth.
3. Moderate Complexity + Advanced Skills (In-House Data Scientists)
When an organization encounters moderate complexity in data analysis and possesses advanced in-house skills, the recommended approach is Simple Data Analysis. SDA is effective for general questions and basic insights.
- Challenges: Balancing the use of advanced skills with simpler tools.
- Goals: Utilize advanced skills for more complex insights.
- Recommendation: IDA will allow your team to fully utilize their skills, uncover deeper insights, and handle complex analytical challenges more effectively.
4. Highly Complex + No In-House Skills
When an organization faces highly complex data analysis requirements and lacks internal expertise, the recommended approach is Intelligent Data Analysis. Due to the lack of internal skills, seeking help from external experts might be a beneficial solution.
- Challenges: Difficulty in analyzing complex data without expertise.
- Goals: Develop foundational data analysis capabilities.
- Recommendation: Use external expertise. DataNorth offers custom solutions and supervision of artificial intelligence projects.
5. Highly Complex + Basic Skills
When an organization encounters highly complex data but only has basic skills, the recommended approach is training the team to use Intelligent Data Analysis).
- Challenges: Insufficient skills to tackle complex data analysis.
- Goals: Bridge the skill gap to enable effective analysis.
- Recommendation: Use SDA for initial insights and seek external training and consulting to enhance skills in using artificial intelligence in data science.
6. Highly Complex + Advanced Skills (In-House Data Scientists)
When an organization encounters highly complex data and has advanced in-house skills, the recommended approach is Intelligent Data Analysis. IDA is suitable for specific and complicated questions and provides detailed insights.
- Challenges: Ensuring advanced skills are utilized effectively.
- Goals: Leverage in-house expertise for deeper analysis.
- Solution: Utilize IDA and get external guidance for out-of-the-box solutions and suggestions.
Making the Choice: Simple vs. Intelligent Data Analysis
To summarize, there is no specific answer for the question which option might be better.
Choosing between the two methods requires careful consideration of your organization’s needs. When in need of a thorough, large volume of data analysis using artificial intelligence as a tool is a ground-breaking method for achieving desired information.
However, if your organization is in need of basic, not complicated analysis cases, it is possible that using simple, traditional analysis techniques might be sufficient and cost-effective. At DataNorth, we’re committed to helping you navigate this decision-making process. With our expert AI assessments and custom AI solutions, you can enhance your data analysis capabilities and drive your organization forward.