The Data Protection Impact Assessment
In today’s world, privacy is more important than ever. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict rules for how organisations should handle personal data. One important tool to ensure compliance is the Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA).
What is a DPIA?
A DPIA is a structured process that helps analyse and minimise the privacy risks of a project that is processing personal data. By examining how you intend to collect, store, use, and delete personal data, a DPIA helps identify potential issues before they become serious problems.
Why is a DPIA important?
Beyond being a legal requirement in certain situations, conducting a DPIA offers several benefits:
- Legal compliance: DPIAs help you meet GDPR obligations. Good documentation is essential, and failing to conduct a required DPIA could result in fines or enforcement action.
- Risk management: They allow you to identify and reduce risks like data breaches or unauthorised access early on.
- Improving project design: Understanding data risks from the start often leads to simpler, more effective solutions.
- Building trust: Showing that you take data privacy seriously helps earn the trust of customers, employees, and other stakeholders.
When is a DPIA required?
Under the GDPR, a DPIA is mandatory when data processing is likely to result in a high risk to the rights of an individual, especially when introducing new technologies.
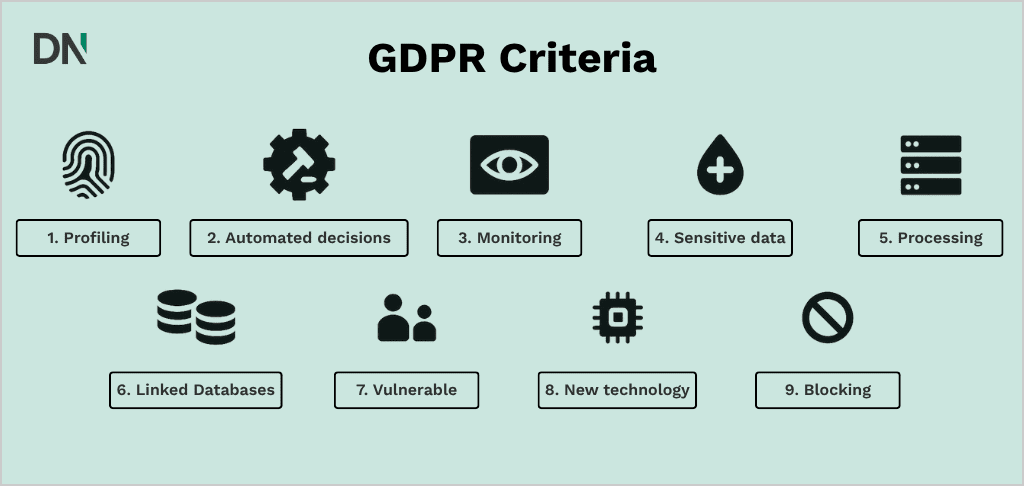
For processing activities organizations can use 9 criteria developed by European supervisory authorities. As a rule of thumb, a DPIA is needed when two or more of these criteria are met:
- Evaluation of individuals based on personal characteristics – including profiling and predictions
- Automated decision-making – with legal or similarly significant consequences
- Systematic and large-scale monitoring – especially in public spaces
- Sensitive data – special categories and criminal data
- Large-scale data processing
- Linked databases – combination of different data collections
- Data of vulnerable individuals – such as employees, children, and patients
- Use of new technologies – with potentially unknown privacy risks
- Blocking of a right, service, or contract – for example, in credit assessments
How to conduct a DPIA?
What are the minimum requirements for a DPIA?
Although organizations can choose their own method for their DPIA, they must include at least the following elements according to the GDPR:
- Systematic description of the intended data processing and purposes
- Assessment of necessity and proportionality of the processing
- Assessment of privacy risks for data subjects
- Intended measures for addressing risks and demonstrating GDPR compliance
When should a DPIA be started?
A DPIA must be started as early as possible in the design process, even if not all processing details are known yet. This supports the mandatory principles of privacy by design and privacy by default. Importantly, a DPIA is not a one-time task but a continuous process that requires regular monitoring and adjustments.
How to assess privacy risks and mitigate residual risk?
When assessing privacy risks, organizations must pay special attention to residual risks – serious situations that may still occur despite precautionary measures. This should indicate:
- Which high privacy risks cannot be completely prevented
- In which specific situations a high residual risk exists
- How likely it is that the described situation will occur
- What damage may arise for the data subjects
Advice and Consultation
Mandatory advisory
Organizations must seek advice from various parties, depending on their specific situation:
- Data Protection Officer (DPO): If appointed, advisory by the DPO is mandatory, including supervision of the DPIA implementation.
- Processor: When a processor processes data on behalf of the organization, they must provide support in conducting the DPIA.
- Data Subjects: Where necessary, data subjects or their representatives must be asked for their opinion through various methods such as surveys, consultation with organizations, or questionnaires.
After the DPIA: Implementation and follow-up
Prior consultation
When the DPIA demonstrates that high residual risks exist, prior consultation with the Data Protection Authority is mandatory before processing can begin.
Publication and transparency
Although not legally required, publication of the DPIA is recommended to increase trust and demonstrate transparency and accountability. This especially applies to processing that affects the general public, such as with government involvement. The published version does not need to contain the complete assessment and can be limited to a summary of the key results.
Continuous monitoring and updates
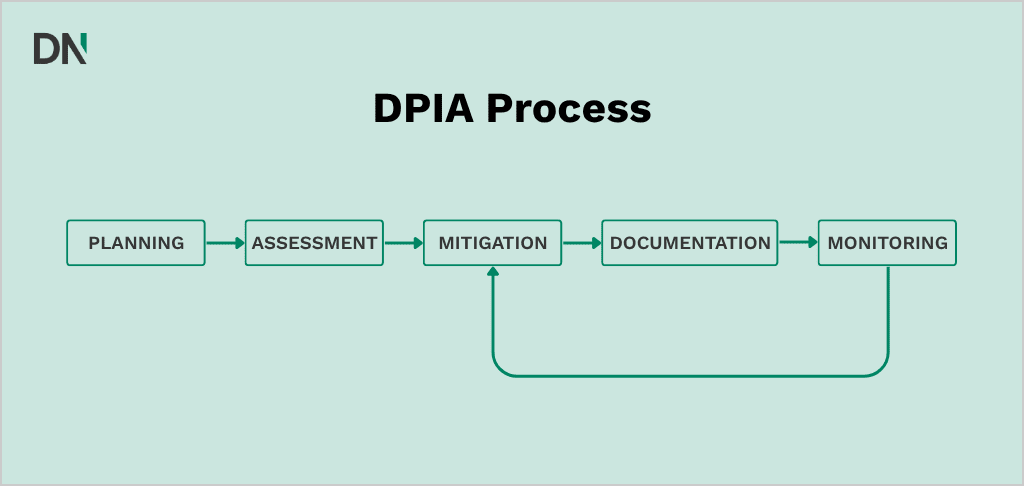
When is a new DPIA needed?
A DPIA requires continuous monitoring and must be updated when there are changes in:
- Data processing itself – such as new technologies or other purposes
- Processing risks – due to technological developments or new vulnerabilities
- Processing context – due to organizational or societal changes
Periodic review
Even without specific changes, it is recommended to conduct a DPIA at least once every three years to ensure the assessment remains current.
Conclusion
The DPIA forms a fundamental part of responsible data processing under various legislation. By proactively identifying privacy risks and implementing appropriate measures, organizations can not only comply with their legal obligations but also strengthen the trust of data subjects. The continuous nature of this process emphasizes the importance of structural attention to privacy within organizations, with transparency and accountability at the center. At Data North, we help organisations integrate privacy and compliance seamlessly into their projects. Our DPIA Assessment ensures that data practices align with GDPR while supporting innovation.