The rise of DeepSeek, a Chinese AI chatbot that has rapidly gained popularity as a low-cost alternative to ChatGPT, has sparked significant concerns about data privacy and security. While the platform offers impressive AI capabilities at a fraction of the cost of its competitors, its data handling practices and security vulnerabilities raise serious questions for users, particularly regarding the protection of personal information and compliance with international privacy regulations. In this article we will get down to the facts and figure out: Is DeepSeek safe to use?
What is DeepSeek?
DeepSeek is a large language model (LLM) developed by Chinese company Hangzhou DeepSeek Artificial Intelligence Co., Ltd. The AI service generates text based on user input and learns from conversations to improve its performance. What sets DeepSeek apart is its claim to deliver advanced AI capabilities at significantly lower costs than American competitors like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, using fewer specialized computer chips. In fact, DeepSeek launched in December 2023 and instantly gained significant traction. In January 2024 this caused the stock price of Nvidia, a company that produces specialized computer chips, to significantly drop by 17% as suddenly it seemed there wasn’t a need for many chips to produce good results.
The platform offers both a web interface and mobile apps, and has become the most downloaded free app on both Apple and Google Play stores in many countries. However, this rapid adoption has come with mounting privacy and security concerns from regulators worldwide.
Does DeepSeek save your data?
Yes, DeepSeek extensively collects and saves user data. According to the official DeepSeek privacy policy, DeepSeek collects information in three main categories:
Information you provide
- Account details: Email address, phone number, date of birth, username, and password
- Content inputs: All text, audio, prompts, uploaded files, and chat conversations
- Support interactions: Identity verification documents, age verification, and feedback
Automatically collected information
- Device data: IP address, unique device identifiers, device model, operating system, and performance data
- Behavioral tracking: Keystroke patterns, system language, usage data, and automatically assigned user IDs
- Network activity: Cookies and payment information
Information from other sources
- Third-party data: Information from social media logins (Google, Apple) and advertising partners
- External tracking: Data about user activities outside the DeepSeek service
Why does DeepSeek collect so much data?
DeepSeek’s extensive data collection serves multiple purposes, similar to other AI platforms but with some concerning differences:
AI training and model improvement
The primary reason for data collection is to train and improve DeepSeek’s AI models. The company uses user inputs and outputs to enhance model performance, reduce “hallucinations” (incorrect or fabricated responses), and develop new features. However, unlike some competitors, DeepSeek provides limited transparency about how users can control this data usage.
Safety and security monitoring
DeepSeek monitors data to prevent abuse, harmful content generation, and to maintain platform stability. The company states it reviews interactions to ensure compliance with usage policies and to protect against misuse.
Service optimization
Data collection helps DeepSeek personalize user experiences, improve response accuracy, and optimize platform performance across different devices and use cases.
DeepSeek data privacy concerns
Storage in China
Perhaps the most significant concern is that all DeepSeek user data is stored on servers located in China. This raises several critical issues:
- Government access: Under Chinese cybersecurity laws, companies are required to provide data access to authorities upon request
- Limited legal recourse: European and American users have little legal protection or recourse for data misuse in China
- Data sovereignty: The transfer of personal data from the EU to China violates GDPR requirements without proper safeguards

GDPR compliance issues
Security experts and regulators have identified numerous GDPR violations in DeepSeek’s operations:
- Lack of transparency: The privacy policy fails to clearly explain data collection practices in local languages
- Missing legal basis: No clear identification of lawful conditions for data processing under Article 6 GDPR
- Inadequate user rights: Limited mechanisms for users to exercise their rights to access, correct, or delete data
- No data protection officer: Absence of required GDPR compliance infrastructure
Consent and user control
DeepSeek’s approach to user consent has raised significant concerns:
- Broad data usage: The privacy policy allows extensive use of user data with limited opt-out options
- Unclear training consent: Users may not fully understand how their data contributes to AI model training
- Automatic data sharing: Information is shared with corporate group entities and advertising partners with minimal user control
Security vulnerabilities in DeepSeek
Multiple security audits have revealed serious vulnerabilities in DeepSeek’s implementation:
Mobile app security flaws
Security researchers have identified critical weaknesses in DeepSeek’s mobile applications. According to NowSecure’s analysis:
- Unencrypted data transmission: Sensitive user data is sent over the internet without encryption
- Weak cryptography: Use of outdated 3DES encryption with hardcoded keys
- Disabled security features: iOS App Transport Security (ATS) is deliberately disabled
- Vulnerable to attacks: High susceptibility to man-in-the-middle attacks and data interception
SecurityScorecard’s STRIKE team analysis revealed additional concerns:
- Hardcoded encryption keys: Cryptographic keys stored directly in app code
- SQL injection vulnerabilities: Potential for database manipulation
- Anti-debugging mechanisms: Attempts to prevent security analysis
- ByteDance integration: Undisclosed connections to TikTok’s parent company
Infrastructure exposures
In early 2025, security researchers discovered a major infrastructure vulnerability:
- Exposed database: A publicly accessible ClickHouse database containing chat histories, API secrets, and operational details
- Full database control: The exposure allowed complete control over database operations without authentication
- Sensitive information leak: Over a million lines of log streams containing user interactions and backend data
AI model vulnerabilities
Security research by Theori found concerning weaknesses in DeepSeek’s AI models:
- Jailbreaking susceptibility: High success rate for attacks that bypass safety measures
- Poor safety performance: Failed 61% of knowledge base tests and 58% of jailbreak tests
- Malicious content generation: 11× more likely to produce dangerous outputs than Western alternatives
Regulatory response and bans
The privacy and security concerns surrounding DeepSeek have prompted swift regulatory action across multiple jurisdictions:
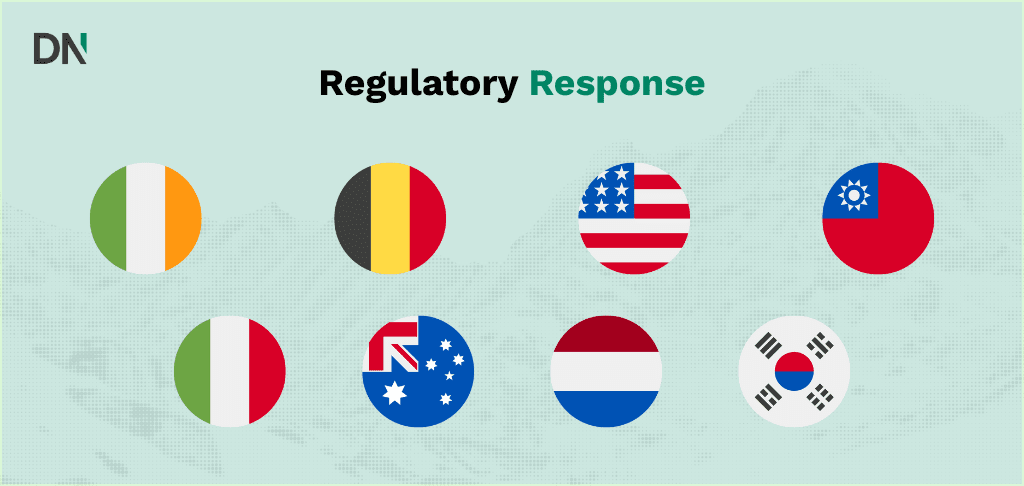
European Union
- Italy: First country to ban DeepSeek, citing GDPR violations and inadequate privacy protections
- Netherlands: Privacy watchdog warned users about uploading personal information
- Ireland and Belgium: Opened formal investigations into DeepSeek’s data practices
Other countries
- Australia: Banned DeepSeek on government devices as an “unacceptable risk” to national security
- South Korea: Found DeepSeek transferred user data without consent and banned the app
- Taiwan: Blocked access due to national security concerns
United States
- Government agencies: NASA, U.S. Navy, and Congressional staff warned against using DeepSeek
- Security concerns: Officials examining potential national security implications
How to use DeepSeek more safely
For users who choose to continue using DeepSeek despite these risks, several protective measures can help minimize exposure:
Data minimization
- Limit personal information: Avoid sharing sensitive personal details, company information, or confidential data
- Use generic queries: Frame questions without revealing personal context or identifying information
- Regular account reviews: Periodically review and delete chat history when possible
Technical protections
- Secure connections: Always use secure WiFi networks or VPNs when accessing DeepSeek
- Device security: Keep devices updated and use additional security software
- Monitor data usage: Be aware of what information you’re providing and how it might be used
Alternative options
- Local models: Consider using locally-hosted AI models that don’t send data to external servers
- European alternatives: Use AI services with better privacy protections and GDPR compliance
- Professional services: For business use, consider AI-as-a-Service providers with proper data protection measures
Business implications and recommendations
Organizations considering DeepSeek should be aware of significant compliance and security risks:
Legal liability
- GDPR violations: Using DeepSeek for customer data processing could expose businesses to regulatory fines
- Data controller responsibility: Companies remain liable for third-party processor violations
- Compliance due diligence: Organizations have a duty to ensure service providers meet data protection standards
Risk assessment
- Sensitive data restrictions: Avoid using DeepSeek for processing personal, financial, or confidential business information
- Industry considerations: Healthcare, finance, and legal sectors face heightened risks
- Contractual limitations: If using DeepSeek, implement strict contractual restrictions on data usage
Alternative strategies
- Privacy-first providers: Choose AI services with transparent privacy practices and local data hosting
- Hybrid approaches: Use DeepSeek only for non-sensitive general queries while maintaining secure alternatives for confidential work
- Professional consultation: Consider AI consultancy services for implementation guidance and risk assessment
The broader context: AI and privacy
The DeepSeek case highlights fundamental tensions in the AI industry between innovation and privacy protection:
Global AI competition
- Cost vs. privacy: The trade-off between affordable AI services and data protection
- Regulatory fragmentation: Different privacy standards across jurisdictions creating compliance challenges
- Technological sovereignty: Countries asserting control over AI technologies and data flows
Industry-wide issues
- Data training ethics: The broader question of using personal data for AI model training without explicit consent
- Transparency challenges: Many AI companies struggle with clear communication about data practices
- User education: The need for better understanding of AI privacy risks among consumers
Conclusion
DeepSeek represents a significant development in the AI landscape, offering advanced capabilities at reduced costs. However, its data privacy and security practices raise serious concerns that users and organizations must carefully consider. The extensive data collection, storage in China, GDPR compliance failures, and security vulnerabilities create substantial risks that may outweigh the platform’s benefits for many use cases.
For individual users, the decision to use DeepSeek should be made with full awareness of the privacy trade-offs involved. Personal and sensitive information should never be shared with the platform, and users should consider whether the convenience justifies the potential risks to their data privacy.
For businesses, the risks are even more pronounced. The potential for GDPR violations, data breaches, and regulatory scrutiny makes DeepSeek unsuitable for most commercial applications, particularly those involving customer data or sensitive business information.
The regulatory responses from multiple countries demonstrate that concerns about DeepSeek are not merely theoretical but represent genuine risks to user privacy and national security. As the AI industry continues to evolve, the DeepSeek case serves as an important reminder that innovation must be balanced with robust privacy protection and regulatory compliance.
Organizations should prioritize AI solutions that demonstrate clear commitment to data protection, transparency, and user rights. While DeepSeek may offer attractive features and pricing, the privacy and security costs may be too high for responsible deployment in most contexts.
For those requiring AI assistance with privacy protection, consider exploring alternatives that offer better data governance, local processing options, or consulting with privacy-focused AI service providers who can help navigate these complex considerations safely and compliantly.