At the beginning of the rise of generative AI, most attention was on “prompt engineering.” This means figuring out the perfect way to phrase a question or request to get the best response from the model. However, as companies start using AI more seriously and on a larger scale, another important area has come into focus: Context Engineering.
While prompt engineering is about how you ask something, context engineering is about what the AI knows when you ask. It involves carefully organizing and managing the information surrounding a large language model (LLM) so that the responses it gives are accurate, relevant, and aligned with business goals.
What is Context Engineering?
In simple terms, it’s about designing and managing the data, instructions, and background information provided to an AI model when it generates answers (“Context window“). Unlike a human worker who knows your company’s products, voice, and customer background, an LLM like GPT-5.2 or Claude 4.5 doesn’t have that knowledge built-in. Context engineering works to fill that gap by creating systems that can pull in relevant data, documents, and past interactions right when they’re needed.
The aim here is to turn a basic reasoning model into a specialized expert in your field without the expense and effort of starting from scratch.
The three layers of context
A successful context engineering plan usually covers three key layers of information:
- System context: This is the set of guidelines that defines how the AI should function, including its behavior and ethical standards. For instance, it might state that the AI is a customer support agent for a specific company and should never give financial advice.
- Retrieval context: This involves accessing real-time data from various sources, like PDFs or databases, to give the AI up-to-date information when responding. Techniques such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) are used for this.
- Session context: This refers to keeping track of the conversation history, allowing the model to remember what has been said in prior interactions.
It’s important to note that context engineering isn’t about retraining the model itself; it’s about fine-tuning the data input to improve the quality of the output. To do this well, you need a mix of data science, software development skills, and an understanding of language.
Key aspects of context engineering
Effective context engineering requires a blend of data science, software architecture, and linguistic strategy.
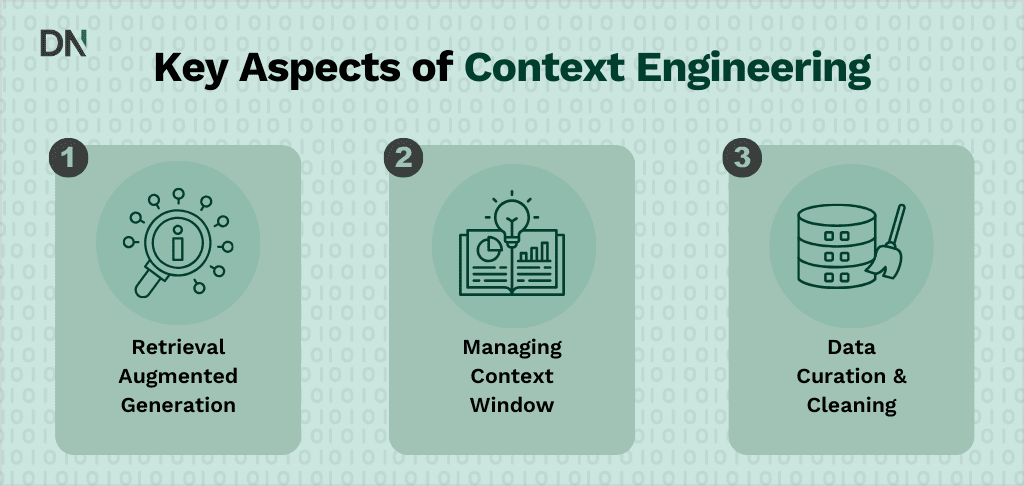
1. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG is the technical backbone of most context engineering strategies. It allows the AI to “look up” information before answering. When a user asks a question, the system first queries a vector database to find relevant company documents, then pastes those documents into the context window along with the user’s question.
Implementing high-performance RAG requires specialized Generative AI development to ensure the retrieved data is actually relevant. Poor retrieval leads to “garbage in, garbage out.”
2. Managing the context window
Every LLM has a “context window”. This is a strict limit on how much text it can process at once (measured in tokens). While newer models like Google’s Gemini 1.5 Pro boast massive context windows (up to 1 million tokens), filling them indiscriminately is dangerous.
Researchers have identified the “Lost in the Middle” phenomenon, where LLMs tend to ignore information buried in the middle of a large block of text, focusing primarily on the beginning and the end. A skilled context engineer structures data to mitigate this, placing critical instructions where the model is most likely to “pay attention.”
3. Data curation and cleaning
Context engineering begins long before the prompt is sent. It starts with data readiness. If your knowledge base contains outdated PDFs or conflicting policies, something can happen that is referred to as AI hallucination or it can provide incorrect answers. An AI feasibility assessment is often the first step to determining if your data infrastructure is ready to support context engineering.
Context Engineering vs. Prompt Engineering
These two terms are often confused, but they serve different roles in the AI stack.
Prompt Engineering is the act of refining the instruction. It is user-facing and tactical.
Context Engineering is the act of refining the environment. It is system-facing and strategic.
Think of the LLM as a brilliant university student taking an exam:
- Prompt Engineering is writing a clear, unambiguous exam question.
- Context Engineering is providing the student with the correct textbooks, reference notes, and calculator before the exam starts.
Comparison: Prompt vs. Context
| Feature | Prompt Engineering | Context Engineering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary focus | The phrasing of the query. | The data available to answer the query. |
| Scope | Single interaction (tactical). | Full system architecture (strategic). |
| Main goal | Elicit a specific style/format. | Ensure factual accuracy and grounding. |
| Scalability | Low (hard to manual prompt for every edge case). | High (automated data retrieval). |
| Required skills | Linguistics, logic, iteration. | Data engineering, vector search, API integration. |
For organizations looking to upskill their teams, a Prompt Engineering Workshop is excellent for individual productivity. However, building a company-wide AI solution requires an Artificial Intelligence Strategy that prioritizes context engineering.
Why Context Engineering matters
Context engineering is the differentiator between a fun demo and a reliable business tool.
1. Reducing hallucinations
Hallucinations often occur when a model is forced to guess because it lacks information. By engineering the context to include the exact facts required (e.g., “The current price of Product X is €50”), you constrain the model to reality. This is critical for industries requiring high compliance, where an AI Compliance audit might be necessary.
2. Overcoming knowledge cutoffs
LLMs are frozen in time; they only know what they learned during training (which might have ended months ago). Context engineering injects real-time data like stock prices, inventory levels, or today’s news, allowing a “frozen” model to act on current information.
3. Data security and privacy
Context engineering acts as a firewall. Instead of letting an employee paste sensitive data into a public model, a secure context pipeline allows you to anonymize data or filter what enters the context window. For highly sensitive data, organizations often pair context engineering with Local LLM consultancy to keep the entire context processing on-premise.
Implementing Context Engineering
Building a system that intelligently manages context involves several steps:
- Vectorization: Converting your knowledge base (docs, wikis) into mathematical vectors.
- Storage: Using vector databases (like Pinecone, Weaviate, or Milvus) to store this knowledge.
- Orchestration: Building workflows that connect the user input, the database, and the LLM. Tools like n8n are powerful here; see our n8n Workflow Automation Package for how to automate these pipelines without heavy coding.
- Optimization: Continuously testing which chunks of data yield the best answers and adjusting the “chunk size” (how much text is retrieved).
Conclusion
As AI models become commodities, the competitive advantage will not belong to those who use the best model, but to those who provide the best context. Context engineering is the mechanism that grounds AI in your unique business reality, transforming it from a generic chatterbox into a precise, reliable enterprise asset.
For leaders looking to move beyond simple prompting and build robust, data-aware AI systems, focusing on the engineering of context is the necessary next step.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between RAG and context engineering?
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is a specific technique used within context engineering. Context engineering is the broader discipline that includes RAG, but also involves managing system prompts, conversation history, and token optimization strategies.
Can context engineering fix a bad model?
To an extent. A smaller, less capable model (like Llama 3 8B) can often outperform a massive model (like GPT-4) if the smaller model is given perfect context and the larger model is given none. However, the model still needs basic reasoning capabilities to understand the context provided.
Does context engineering require coding?
Yes. While prompt engineering can be done in a chat interface, context engineering requires building data pipelines, API connections, and retrieval logic. This typically requires Machine Learning development expertise.
Is context engineering expensive?
It can be. Adding more text to the context window increases token usage, which increases cost and latency. Effective context engineering involves finding the balance between providing enough information to be accurate and keeping the context concise to control costs.